- The Deep View
- Posts
- ⚙️ ChatGPT can finally do your work for you
⚙️ ChatGPT can finally do your work for you

Welcome back. Trump's upcoming 20-page AI action plan primarily focuses on conveying a "hands-off, pro-growth approach" with aspirational goals, including promoting innovation and reducing regulatory burdens. But the real action is in the executive orders being drafted, including one led by AI czar David Sacks to combat "woke" AI by requiring the government to acquire only "neutral" technology. Nothing says "hands-off government approach" quite like mandating ideological purity in your AI purchases.
In today’s newsletter:
💊 Quantum-enhanced drug discovery
🤖 Could robots grow by consuming other robots?
🎬 ChatGPT agent enters the action era
💊 Quantum-enhanced drug discovery

Source: IBM
Moderna and IBM researchers have achieved what they're calling a record-setting breakthrough in using quantum computers to predict how mRNA molecules fold — a critical step in designing effective RNA-based medicines.
The collaboration, detailed in IBM's newly published case study, demonstrated quantum algorithms successfully predicting the 3D shape that mRNA takes when it folds in on itself. The team tested this on genetic sequences up to 60 building blocks in length, using quantum processors with 80 quantum bits — the fundamental units of quantum information. According to the researchers, no one had previously simulated sequences of even 42 building blocks on a quantum computer.
The team borrowed a risk-assessment technique from Wall Street trading — typically used to measure how badly an investment portfolio might perform in worst-case scenarios — and adapted it to help quantum computers focus on the most promising molecular shapes while ignoring computational errors. Alexey Galda, Associate Scientific Director of Quantum Algorithms and Applications at Moderna, said this quantum approach offers "a more diverse set of solutions" than traditional computers alone.
A work published in the IEEE International Conference on Quantum Computing and Engineering demonstrated that the quantum method matched commercial software in finding optimal molecular configurations.
Upcoming research, set for publication later this year, tackles even larger problems using 156 quantum bits.
The partnership originated from Moderna's participation in IBM's Quantum Accelerator program, which is part of a broader initiative by pharmaceutical companies to explore quantum computing for drug discovery.
Why it matters: While quantum won't replace traditional computing, Wade Davis, Senior Vice President of Digital at Moderna, said the technology could accelerate the notoriously slow process of drug development. Understanding how mRNA folds is crucial for designing medicines that work effectively without triggering unwanted immune responses, potentially leading to the development of life-saving treatments that reach the market faster.

His First Venture Sold for $120M – This Time’s Different
Austin Allison knows how to use tech to disrupt real estate. His first venture, dotloop, sold for $120M. But he had one nagging regret.
"I always wished everyday people could have invested in dotloop and shared that success," Allison later said.
So he fixed that with Pacaso, his new venture disrupting a $1.3T market. They have $110M+ in gross profit to date, with 41% YoY growth in 2024. They even reserved the Nasdaq ticker PCSO.
And unlike dotloop, you can invest in Pacaso as a private company.
🤖 Could robots grow by consuming other robots?
Source: Midjourney v7
Researchers have developed robots that can physically grow, repair and evolve by consuming other robot parts — a breakthrough that could fundamentally change how machines operate in unpredictable environments.
The system, published this week in Science Advances, uses modular units called Truss Links, lightweight bars with magnetic connectors, that can attach at multiple angles. Individual links can only crawl forward and backward, but when they combine, they form increasingly complex structures.
In testing, six links self-assembled into a walking tetrahedron that picked up a seventh link, boosting its speed by more than 60%. Damaged structures reformed themselves by reconnecting with scattered parts, mimicking the process of biological healing.
The robots start with simple linear movement and evolve into three-dimensional structures without human intervention
Structures like triangles and stars form through crawling, folding and merging — processes that occurred in nearly half of the thousands of randomized simulations
Unlike traditional modular robots, these don't require external tools or new parts to reconfigure
The research team, led by scientists at MIT and Harvard, tested the concept through both physical experiments and computer simulations to identify which formations could emerge autonomously.
Why it matters: Current robots are built for specific tasks and fail when conditions change. This "robot metabolism" approach could enable machines that adapt to new terrain, recover from damage and evolve capabilities we haven't programmed. For space exploration, disaster response and environments where human repair isn't possible, robots that can rebuild themselves using available materials could be transformative.

Want To Stay On Top Of The Latest SMB Trends?
Look no further. Salesforce, the premier CRM platform, doesn't just offer powerful AI CRM solutions; they also keep you on the cutting edge of the small business world.
Their newest report keeps you informed with the latest SMB insights.
Inside you’ll find insights from over 3,000 small and medium business leaders, including how they’re building their tech stacks, how they’re leveraging AI to boost revenue and efficiency, and their biggest priorities (and challenges) for the upcoming year.


Uber bets big on robotaxis with Lucid and a $300M EV push
AI funders pledge $1B to support frontline workers
AI start-up Perplexity’s valuation tops $18bn months after latest funding round
OpenAI wants a cut of your ChatGPT shopping habits
Lovable hits unicorn status with $200M just 8 months in
This AI warps live video in real time
Delta to eliminate set prices in favor of AI that determines personalized ticket pricing
Ride-hailing giants’ electric promises are stalling worldwide
Nvidia chief vows to ‘accelerate recovery’ of China sales as H20 chip ban lifted

Senior machine-learning talent available this month
Brought to you by Athyna.
Camila, Lima: Senior ML engineer with 9 years in predictive analytics, 4 years optimizing generative-AI workflows, GCP certified — $47/h
Bruno, Santiago: AI specialist with 8 years in recommender systems, 3 years integrating foundation models into production APIs — $49/h
Renata, Montevideo: Computer-vision lead with 10 years building detection pipelines, 2 years applying CLIP and Segment Anything — $44/h

🎬 ChatGPT agent enters the action era

Source: OpenAI
For the first time, ChatGPT can actually do your work for you. OpenAI's new Agent mode enables tasks to be completed autonomously using its own virtual computer. Ask it to analyze three competitors and build a slide deck, plan a Japanese breakfast for four people and purchase the necessary ingredients, or scan your calendar and provide a brief on upcoming meetings based on recent news. Then walk away while it works.
The new agent mode combines three existing tools into a single system that can fluidly switch between thinking and acting. It merges Operator's ability to click and navigate websites, Deep Research's skill at synthesizing information from multiple sources, and ChatGPT's conversational reasoning abilities.
Previous AI agents from Google, Perplexity and other competitors struggled with complex, multi-step tasks. ChatGPT Agent operates through its own virtual computer, which provides access to visual and text browsers, code execution terminals and connected apps, such as Gmail or GitHub.
The system delivered strong results across key industry benchmarks, often approaching or exceeding human performance:
41.6% on Humanity's Last Exam, roughly double the performance of OpenAI's o3 model
27.4% on FrontierMath, compared to just 6.3% for previous models
78.2% on WebArena, approaching the 80%+ human baseline for real-world web navigation
71.3% on investment banking modeling tasks, significantly outperforming both Deep Research and o3
While OpenAI pushes toward general-purpose autonomy, competitors are taking different approaches. Reflection's Asimov agent, developed by former Google researchers, focuses specifically on understanding software development by ingesting company data and documentation. The contrast highlights a fundamental split: OpenAI's broad toolkit approach versus specialized agents that excel in narrow domains.
Previous attempts at developing general-purpose agents have proven challenging when interacting with the real world. ChatGPT Agent introduces new risks as OpenAI's first system that can take web actions, prompting comprehensive safety measures including explicit user confirmation before consequential actions, active supervision for critical tasks and built-in prompt injection defenses.
The tool launches with usage limits: Pro subscribers ($200/month) get 400 queries monthly, while Plus and Team users receive 40. Current limitations include rudimentary slideshow formatting and unavailability in the European Economic Area.

We've been hearing about AI agents for years, and they've often failed to meet expectations. ChatGPT Agent may actually be able to maintain context across tools and delivering genuinely useful results on real work.
The smart play here is OpenAI's bet on breadth over specialization. While startups like Reflection are training agents to deeply understand specific workflows, OpenAI is building a Swiss Army knife that can tackle whatever you throw at it. The benchmark scores back this up, but what matters more is that it doesn't fall apart when tasks get messy.
We’ll be testing it out heavily this weekend and report back on any findings on Monday.


Which image is real? |
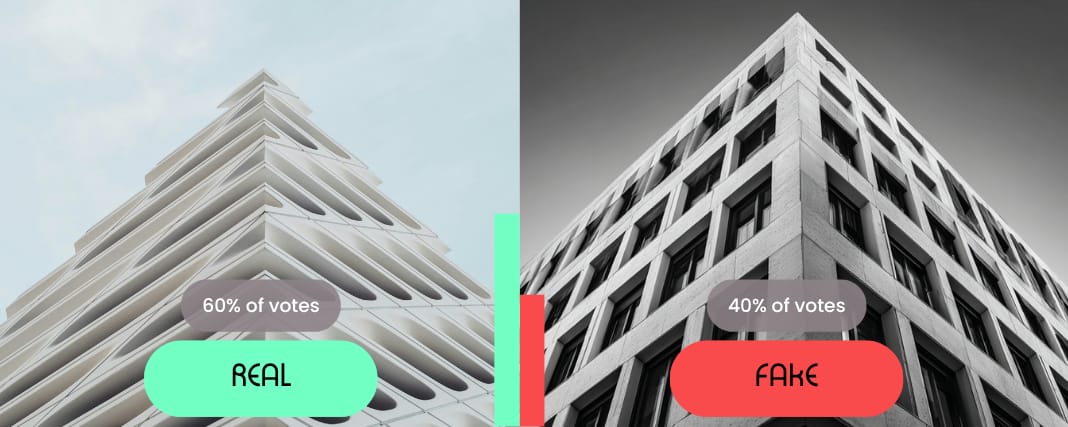



🤔 Your thought process:
Selected Image 1 (Left):
“I know that building, I think, and the other image looks just a tad too polished, but it’s probably because I know this building. It’s like looking at the Broad.”
“The overly futuristic look of [this image] threw me off for a second, but the weird placement of the windows on the top middle/right of [other image] made me rethink that [this] was the correct one.”
Selected Image 2 (Right):
“Ha! I asked ChatGPT which image was real - and it told me that [the other image] was a digital rendering. Further, it did a real world search to try and find photos that matched that building and it could not do so - reinforcing its incorrect choice.”
“Lots of detail and more normal appearance led me to believe it was real.”
💭 A poll before you go
Which use case for ChatGPT Agent would you try first? |
The Deep View is written by Faris Kojok, Chris Bibey and The Deep View crew. Please reply with any feedback.
Thanks for reading today’s edition of The Deep View! We’ll see you in the next one.
P.S. Enjoyed reading? Take The Deep View with you on the go! We’ve got exclusive, in-depth interviews for you on The Deep View: Conversations podcast every Tuesday morning. Subscribe here!
P.P.S. If you want to get in front of an audience of 450,000+ developers, business leaders and tech enthusiasts, get in touch with us here.
*Indicates sponsored content
*Pacaso Disclaimer: This is a paid advertisement for Pacaso's Regulation A offering. Please read the offering circular at invest.pacaso.com. Reserving the ticker symbol is not a guarantee that the company will go public. Listing on the Nasdaq is subject to approvals.